Kubernetes overview¶
Kubernetes (also known as K8s) is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It was originally developed by Google and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
Kubernetes allows developers to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications across a cluster of nodes, providing features such as load balancing, automatic scaling, self-healing, and rolling updates. It provides a declarative way to define the desired state of an application and ensures that the actual state matches the desired state.
Kubernetes is highly modular and extensible, with a large ecosystem of plugins and tools that can be used to customize and extend its functionality.
To make things easier for you, we have introduced Kubernetes monitoring in FusionReactor Cloud. With this tool, you can automate many of the manual tasks and focus on getting the most out of your Kubernetes monitoring. Whether you're an SRE, application developer, or DevOps administrator, Kubernetes monitoring in FusionReactor Cloud can help you troubleshoot incidents, implement changes, and maintain servers more easily.
Learn more
Benefits¶
-
Real time alerts. Monitoring Kubernetes clusters in real-time can detect errors early and send alerts to you immediately. This saves your brand's reputation and reduces service restoration time.
-
Workload optimization. Monitoring your Kubernetes cluster can help you manage workloads better and optimize resource usage. This can lead to better performance and reliability.
-
Troubleshoot with ease. Monitoring can assist in troubleshooting by accessing logs and discovering root causes of issues. This can minimize downtime and reduce the workload for developers.
-
Real time visibility. Monitoring your Kubernetes cluster helps you track costs in real-time. It lets you see how many nodes, load balancers, and persistent volumes are deployed and the cost incurred from each.
-
Powerful insights. Kubernetes monitoring provides unique insights into how users interact with your application, helping you improve future product decisions. It also helps in identifying features that need expansion or improvement.
Clusters or pods?¶
A Kubernetes cluster and a pod are two different concepts in Kubernetes architecture.
A Kubernetes cluster is a group of nodes that work together to run containerized applications. The cluster consists of a master node that manages the cluster, and one or more worker nodes that run the containers. The master node is responsible for scheduling containers, monitoring their health, and managing their lifecycle. The worker nodes are where the containers actually run and execute their processes. The cluster provides a high-level abstraction for managing and scaling containerized applications, and provides features such as load balancing, service discovery, and automatic failover.
A pod, on the other hand, is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. It is a logical host for one or more containers, and represents a single instance of a running process. Pods are used to encapsulate and manage the runtime environment for a container, including its network and storage resources. Multiple containers can be co-located within a pod and share the same network namespace, allowing them to communicate with each other using localhost.
In summary, a Kubernetes cluster is a group of nodes that work together to run containerized applications, while a pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes that represents a single instance of a running process and encapsulates the runtime environment for one or more containers.
Kubernetes dashboards¶
Kubernetes monitoring with FusionReactor Cloud includes many dashboards out of the box to help you get started with observing and monitoring your Kubernetes clusters and their workloads. This set includes the following:
-
Kubernetes / API server
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Multi-Cluster
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Cluster
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Pods)
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Workloads)
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Node (Pods)
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Pod
-
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Workload
-
Kubernetes / Controller Manager
-
Kubernetes / Kubelet
-
Kubernetes / Networking / Namespace (Pods)
-
Kubernetes / Networking / Namespace (Workload)
K8s dashboard spotlight¶
Our FusionReactor Kubernetes monitoring integration gives you visibility into your Kubernetes clusters and workloads within minutes, whether your clusters are hosted on-premises or in the cloud. Below are just two of our Kubernetes dashboards that will allow you to monitor your telemetry data by navigating through your nodes and pods to evaluate their health.
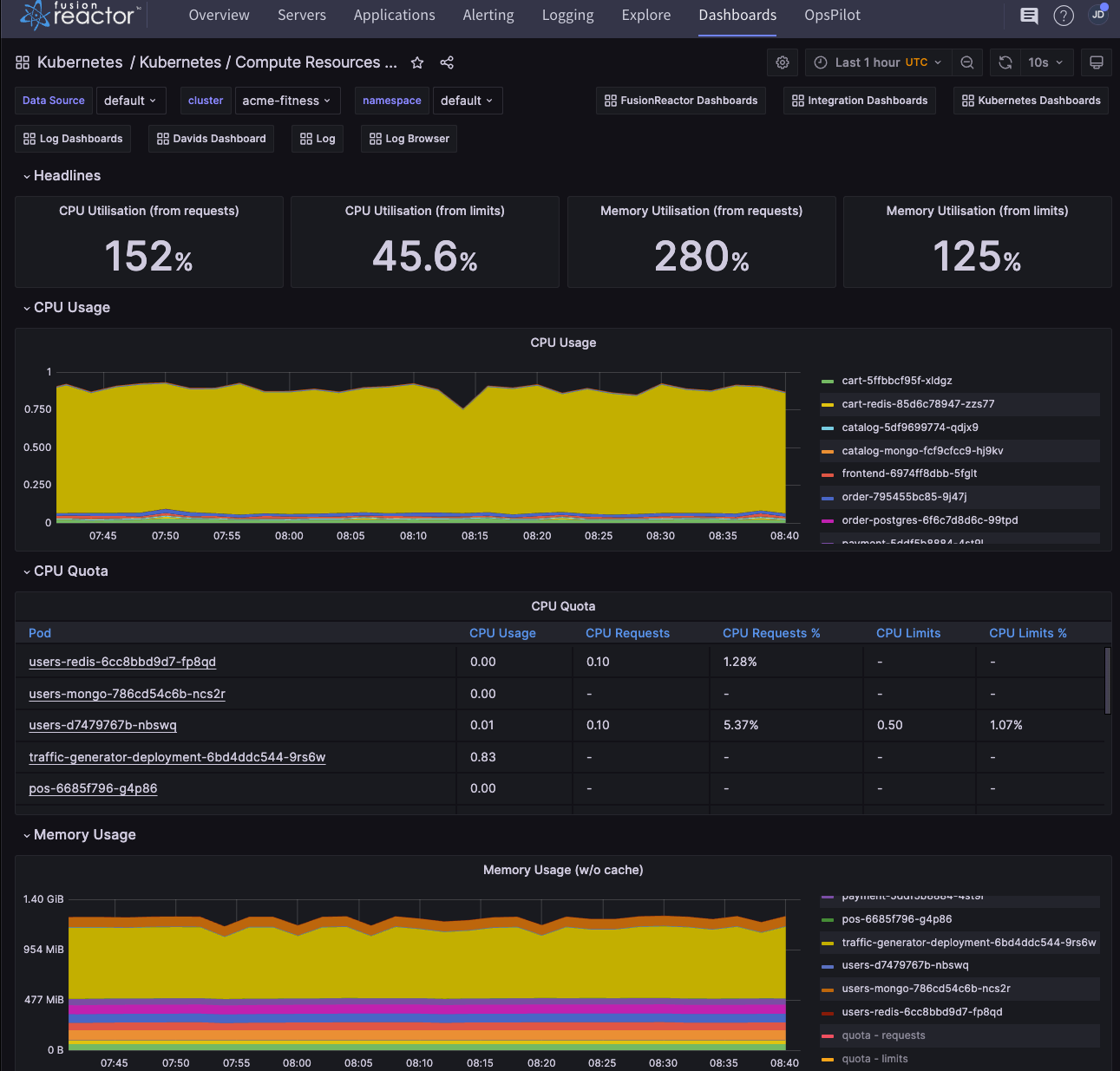
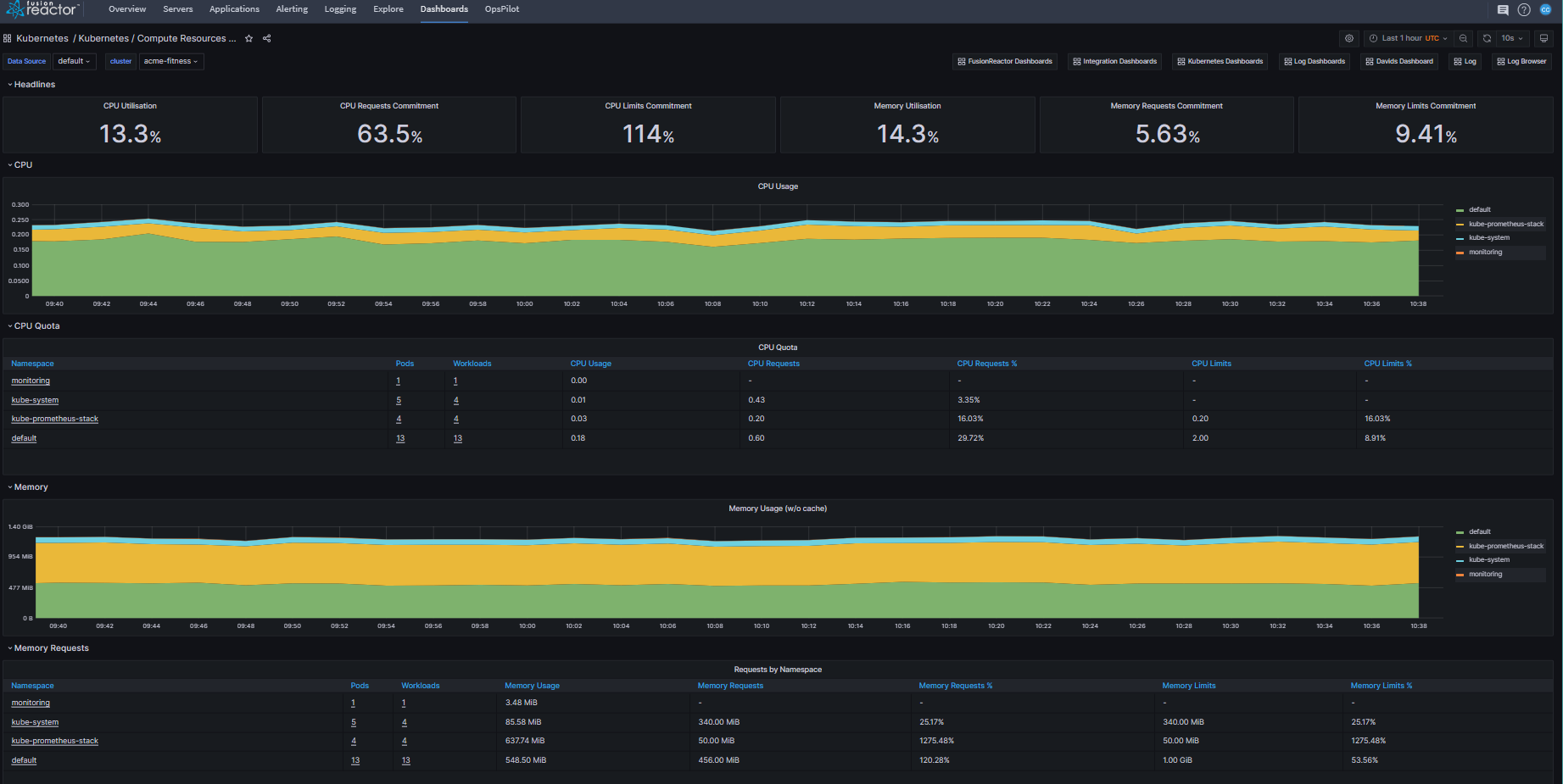
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Cluster¶
An easy-to-scan overview of the performance and resource demands of the different tenants in a cluster.
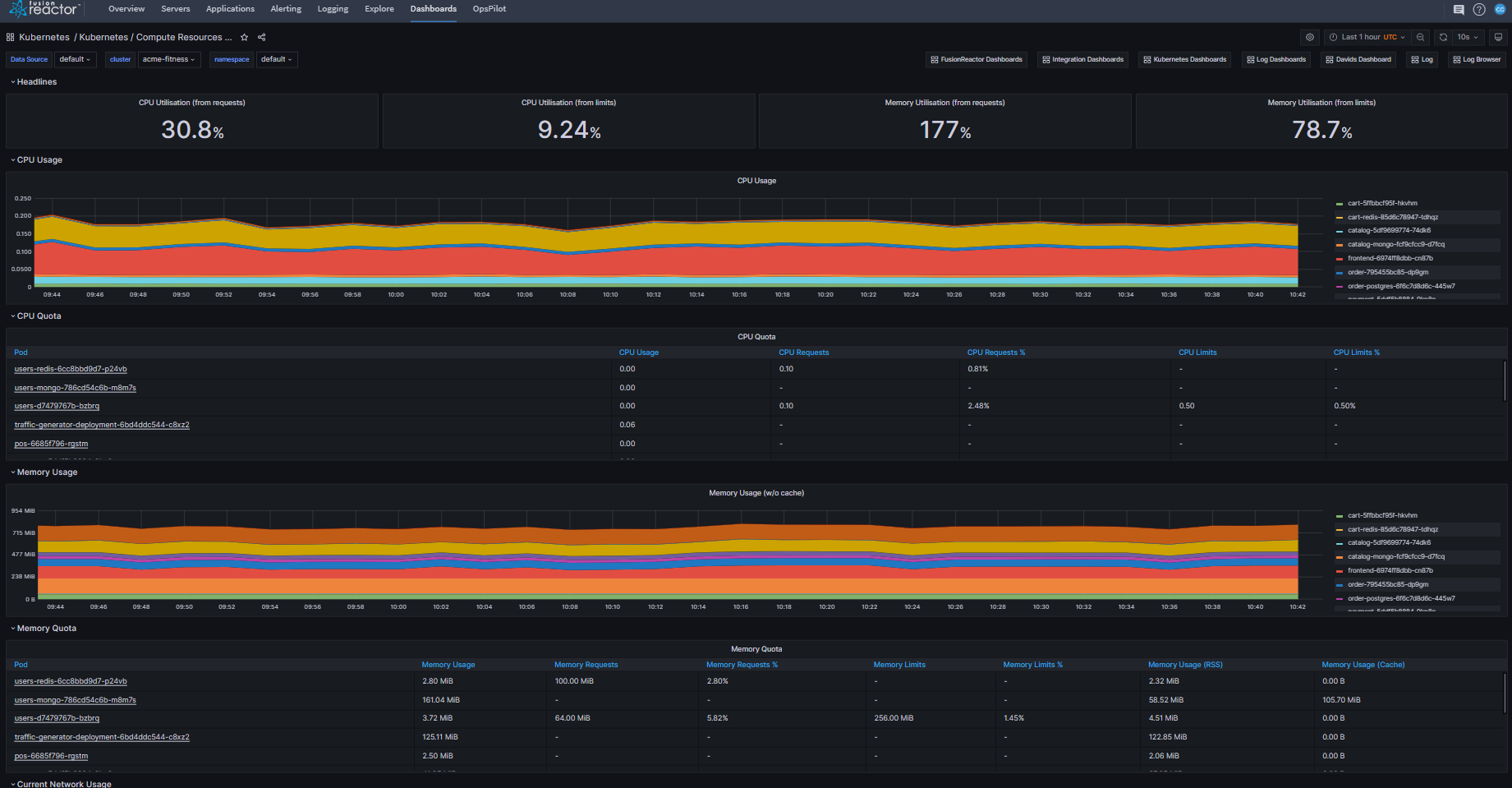
Kubernetes / Compute Resources / Namespace (Pods)¶
Displays the resource demand for each individual pod, broken down per namespace.
Need more help?
Contact support in the chat bubble and let us know how we can assist.